
It is simple to diagnose these abnormalities at the time of routine well puppy exams or spay and neuter appointments. Preeruption radiographs are most diagnostic after 8 to 10 weeks of age. In some breeds, such as the Doberman Pinscher, Rottweiler, and German Shepherd Dog, absence of teeth may be grounds for elimination in the show ring because of the hereditary component of this problem.
Canine teeth diagram full#
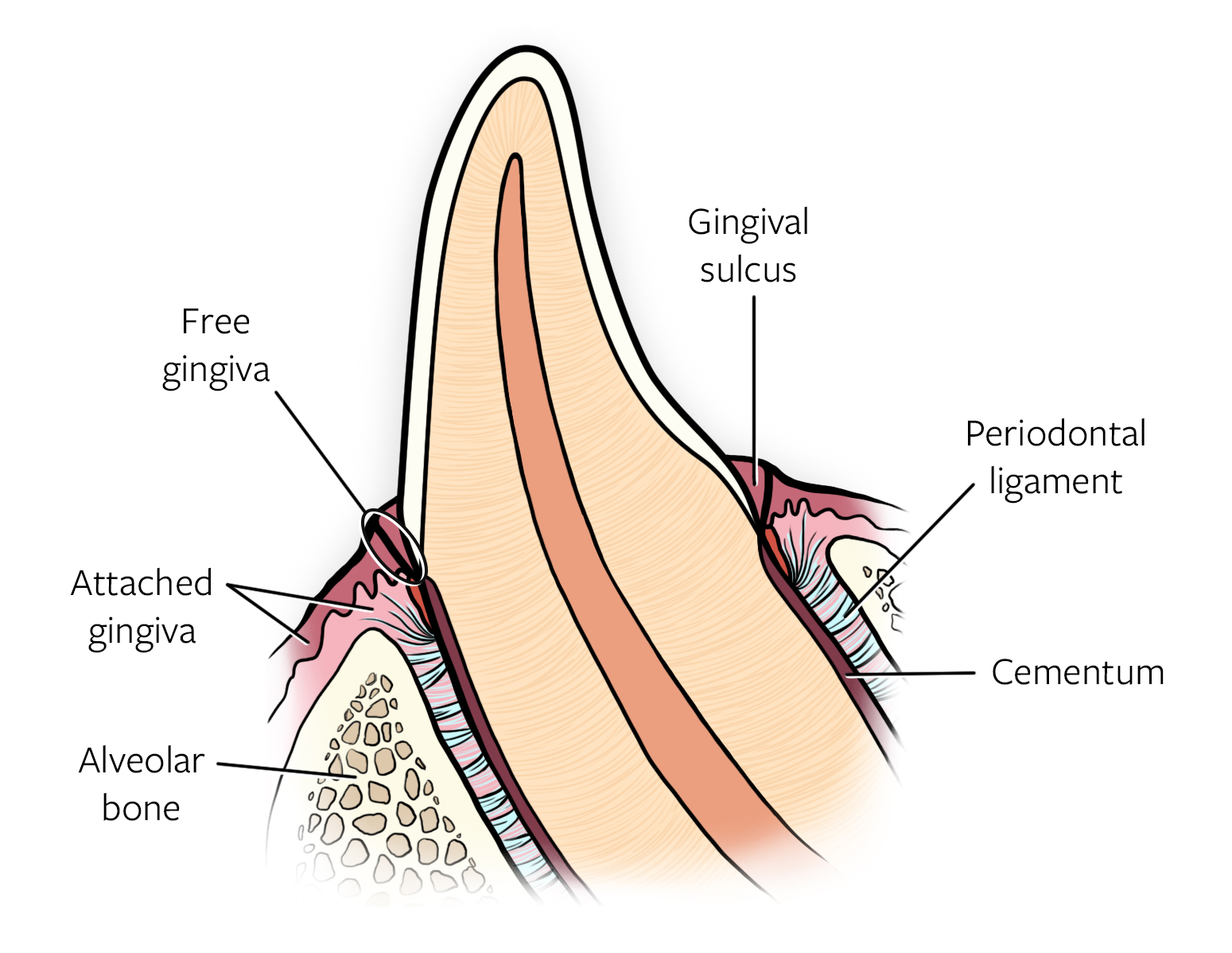
All puppies and kittens should be monitored for full dentition by 6 months of age, and abnormalities should be investigated radiographically.īreeders may request preeruption dental radiographs to determine whether a particular dog has a full complement of permanent teeth. Timely diagnosis and treatment early in life could have prevented the extensive damage and tooth loss caused by this pathology. When performing deciduous tooth extractions, special care should be exercised to avoid trauma to the permanent tooth bud as this can cause damage to the permanent tooth enamel ( Figure 35-5).įigure 35-8 Radiograph of a dentigerous cyst caused by an impacted right lower first premolar in a 5-year-old Japanese Chin. Postoperative dental radiographs should be obtained to ensure complete extraction. Incomplete extraction may lead to infection, pain, or malocclusion. It is essential to remove the entire deciduous tooth root when extraction is performed. Extraction techniques are covered in detail in other texts (see Suggested Reading list) however, it is important to note that deciduous teeth have deceptively long roots compared with crown size, very thin enamel walls, and break easily with overzealous extraction technique ( Figure 35-4). A gingival flap may be appropriate to allow adequate visualization and minimize chance of root fracture. Preoperative intraoral dental radiographs identify location and shape of the tooth to be extracted. Treatment for persistent deciduous teeth consists of complete extraction of the deciduous tooth. Left untreated, these teeth develop severe periodontal problems over time, which can result in oronasal fistulas. This is also called a lance canine tooth. Figure 35-3 Photos of the left upper arcade in a Beagle dog showing a persistent deciduous canine that has caused the permanent canine tooth to erupt mesially.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
